1. Is jQuery a framework or a library?
- A framework is something that usually forces a certain way of implementing a solution, whereas jQuery is just a tool to make implementing what you want to do easier.
- A library is a collection of functions which are useful when writing web apps. Your code is in charge and it calls into the library when it sees fit. Example is jQuery.
- Frameworks is a particular implementation of a web application, where your code fills in the details.
- The framework is in charge and it calls into your code when it needs something app specific.
2. The features provided by jQuery

- The purpose of jQuery is to make it much easier to use JavaScript on your website.
- jQuery takes a lot of common tasks that require many lines of JavaScript code to accomplish, and wraps them into methods that you can call with a single line of code.
- jQuery also simplifies a lot of the complicated things from JavaScript, like AJAX calls and DOM manipulation.
- HTML/DOM manipulation
- CSS manipulation
- HTML event methods
- Effects and animations
- AJAX
- Utilities
3. The advantages and disadvantages of using jQuery
➤ Advantages
- The main advantage of jQuery is that it is much easier than its competitors.
- You can add plugins easily, translating this into a substantial saving of time and effort.
- In fact, one of the main reasons why Resig and his team created jQuery was to buy time (in the web development world, time matters a lot).
- The open source license of jQuery allows the library to always have constant and fast support, constantly publishing updates.
- The jQuery community is active and extremely hardworking.
- Another advantage of jQuery over its competitors such as Flash and pure CSS is its excellent integration with AJAX.
- jQuery is flexible and fast for web development
- It comes with an MIT license and is Open Source
- It has an excellent support community
- Bugs are resolved quickly
- It has Plugins
- Excellent integration with AJAX
➤ Disadvantages
- One of the main disadvantages of jQuery is the large number of published versions in the short time.
- It does not matter if you are running the latest version of jQuery, you will have to host the library yourself (and update it constantly), or download the library from Google(attractive, but can bring incompatibility problems with the code).
- jQuery is easy to install and learn, initially. But it’s not that easy if we compare it with CSSIf jQuery is improperly implemented as a Framework, the development environment can get out of control.
5. Selectors
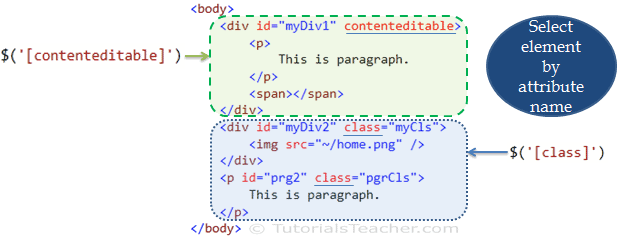
- jQuery selectors allow you to select and manipulate HTML element(s).
- jQuery selectors are used to "find" (or select) HTML elements based on their name, id, classes, types, attributes, values of attributes and much more. It's based on the existing CSS Selectors, and in addition, it has some own custom selectors.
- All selectors in jQuery start with the dollar sign and parentheses: $().
The element Selector
- The jQuery element selector selects elements based on the element name.
- You can select all <p> elements on a page like this:
$("p")
Example
- When a user clicks on a button, all <p> elements will be hidden:
Example
$(document).ready(function(){
$("button").click(function(){
$("p").hide();
});
});
The #id Selector
- The jQuery #id selector uses the id attribute of an HTML tag to find the specific element.
- An id should be unique within a page, so you should use the #id selector when you want to find a single, unique element.
- To find an element with a specific id, write a hash character, followed by the id of the HTML element:
$("#test")
Example
When a user clicks on a button, the element with id="test" will be hidden:
Example
$(document).ready(function(){
$("button").click(function(){
$("#test").hide();
});
});
The .class Selector
- The jQuery .class selector finds elements with a specific class.
- To find elements with a specific class, write a period character, followed by the name of the class:
$(".test")
Example
When a user clicks on a button, the elements with class="test" will be hidden:
Example
$(document).ready(function(){
$("button").click(function(){
$(".test").hide();
});
});
6.1 CSS advanced selectors in jQuery
- Advanced Selectors used in jQuery. UniversalClass. There are numerous selectors that you can use both in CSS and in jQuery. With jQuery, you can use advanced selectors that help you reference various elements in an HTML page and then apply properties and call methods as needed.
6.2 jQuery’s DOM traversal API
- The Document Object Model (DOM) is a programming API for HTML and XML documents. It defines the logical structure of documents and the way a document is accessed and manipulated. In the DOM specification, the term "document" is used in the broad sense - increasingly, XML is being used as a way of representing many different kinds of information that may be stored in diverse systems, and much of this would traditionally be seen as data rather than as documents. Nevertheless, XML presents this data as documents, and the DOM may be used to manage this data.
- The Document Object Model originated as a specification to allow JavaScript scripts and Java programs to be portable among web browsers. Dynamic HTML was the immediate ancestor of the Document Object Model, and it was originally thought of largely in terms of browsers. However, when the Document Object Model Working Group was formed, it was also joined by vendors in other domains, including HTML or XML editors and document repositories. Several of these vendors had worked with SGML before XML was developed; as a result, the Document Object Model has been influenced by SGML Groves and the HyTime standard. Some of these vendors had also developed their own object models for documents in order to provide programming APIs for SGML/XML editors or document repositories, and these object models have also influenced the Document Object Model.
7. The importance of DOM objects
- Rendering/Layout engines (wikipedia links: Gecko for Firefox, WebKit for Safari and Chrome, Trident for IE) traverse the DOM, and and processes elements they understand.
- The aim is to position, represent and render elements according to what it knows inline, or from related CSS. I will conveniently ignore HTML5 Canvas for now. There is a handy comparison on wikipedia of capabilities of the layout engines.
- The rendering/layout engine can only process what it knows. I previously talked of glass-ceilings and used the lack of a ‘image drop-down’ as an example of that. In that case “image drop-down” may be easy for humans to understand but the rendering engine needs it represented in the DOM as a series of regular <div> <ul> <li> <span> items, that are unlike the <select> that is canonical for ‘drop-down’.
- It is like that for every advanced effect, I suggest. Thus to push ahead in terms of capability, the rendering/layout engine needs to be enhanced. There are four main browsers now, meaning that a committee needs to decide what new affortdnces and capabilities the DOM can encode, and that needs to be rendered and interacted with.
- Your web app may have threads of operation that mutate the DOM. That would be for human interactions as well as Javascript (AJAX, COMET etc). Those DOM changes are not immediately processed. The rendering engine kicks in later and processes the changed nodes within the DOM. As such, you should think about the DOM as being an intermediate between the code that requires something to be seen, and the rendering engine that’s going to make that happen.
- By design, the DOM and browsers pertain to presentation and interaction only. There is a server part of the application, that is most likely handling business logic, and persistence.
- The server and browser speak HTTP to each other of course, and therefore the overloaded term thin client applies to this class of application. Another “thin” aspect of this type of application is the lazy way that additional “pages” of the application are retrieved at the time of first use. The whole application is delivered incrementally to the browser, while in use, leading to a hugely important faster start.
8. Benefits of using jQuery

- jQuery is a fast and concise JavaScript Library that simplifies HTML document traversing, event handling, animating, and Ajax interactions for rapid web development. jQuery is designed to change the way that you write JavaScript.
➤ Benefits of using jQuery:
- Search Engine Optimized – While search engines are getting better at being able to read content within some Flash, everything within jQuery is setup as text. This means it is completely readable to all the search engines, exposing all your keyword rich content.
- Save Time – Five lines of jQuery are equivalent to 25 lines of conventional JavaScript code. This means smaller files and faster loading web pages.
- Plug-ins – There are an abundance of plug-ins on the web that make creating special effects simple and fast for web developers.
- Help? – With an abundance of plug-ins comes with an abundance of help. There is a large helpful support community on the web to help you quickly remedy any bug issues.
- That was easy! – jQuery has easy implementation for web developers in comparison to other applications.
- Cross Browser Friendly – jQuery is currently the most popular JavaScript library and works in all browsers.
- FREE! – free, open source software.
- Mobile Devices – jQuery is supported by any mobile device whose web browser supports JavaScript. A lot of mobile devices like iPads and iPhones don’t run Flash at all.
- Simplifies AJAX
- Wow Factor – Web developers use jQuery to make web pages more exciting, interactive, cleaner, and more user friendly. Make your users go WOW!
10. Advanced features provided by jQuery

- In part of being a web designer or front end developer you will commonly run into JavaScript, often referred to as JS, and jQuery. Within the top 10,000 websites JavaScript is used within over 92% of them, and jQuery is used within in over 63% of them. Needless to say, they are fairly popular. You may even aspire to write JavaScript or jQuery to build your own behaviors at one point or another.
- Like CSS, JavaScript should be saved in an external file with the .js file extension, and then referenced within an HTML document using the script element. Where the JavaScript reference is placed with HTML depends on when it should be executed. Generally speaking, the best place to reference JavaScript files is right before the closing </body> tag so that the JavaScript file is loaded after all of the HTML has been parsed. However, at times, JavaScript is needed to help render HTML and determine it’s behavior, thus may be referenced within a documents head.
- The first step to using jQuery is to reference it from within a HTML document. As previously mentioned with JavaScript, this is done using the script element just before the closing </body> tag. Since jQuery is it’s own library it is best to keep it separate from all the other JavaScript being written.
- When referencing jQuery there are a few options, specifically as whether to use the minified or uncompressed version, and as whether to use a content delivery network, CDN, such as Google hosted libraries. If the code being written is for a live, production environment it is encouraged to use the minified version for better loading times. Additionally, using a CDN like Google also helps with loading time, and potential caching benefits.
➤ jquery Object
- jQuery comes with it’s own object, the dollar sign, $, also known as jQuery. The $ object is specifically made for selecting an element and then returning that element node to perform an action on it. These selections and actions should be written in a new file, referenced outside of the actual jQuery library.
➤ Document Ready
- Before trigging any jQuery to traverse and manipulate a page it is best to wait until the DOM is finished loading. Fortunately jQuery has a ready event, .ready(), which can be called when the HTML document is ready to be altered. By placing all of our other custom written jQuery inside of this function we can guarantee that it will not be executed until the page has loaded and the DOM is ready..
➤ Selectors
- As previously mentioned, one of the core concepts of jQuery is to select elements and perform an action. jQuery has done a great job of making the task of selecting an element, or elements, extremely easy by mimicking that of CSS. On top of the general CSS selectors, jQuery has support for all of the unique CSS3 selectors, which work regardless of which browser is being used.
- Invoking the jQuery object, $(), containing a selector will return that DOM node to manipulate it. The selector falls within the parentheses, ('...'), and may select elements just like that of CSS.
➤ Traversing
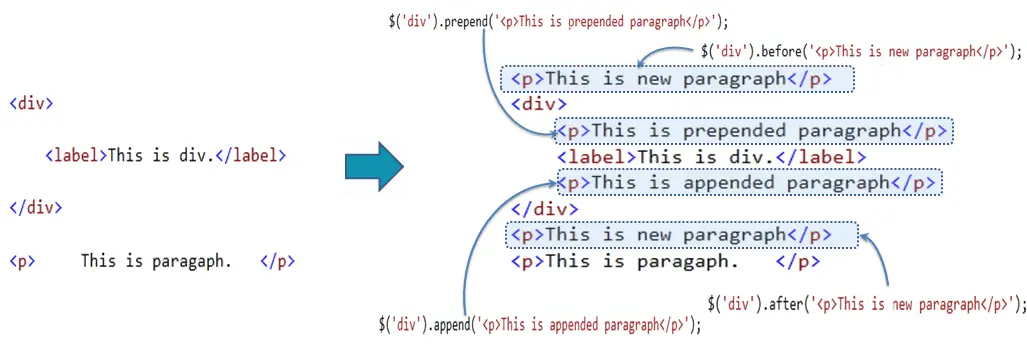
- At times the general CSS selectors alone don’t cut it and a little more detailed control is desired. Fortunately jQuery provides a handful of methods for traversing up and down the DOM tree, filtering and selecting elements as necessary.
- To get started with filtering elements inside the DOM a general selection needs to be made, from which will be traversed from relatively. In the example below the original selection finds all of the div elements in the DOM, which are then filtered using the .not() method. With this specific method all of the div elements without a class of type or collection will be selected.
➤ Changing Methods
- For even more control as to which elements are selected different traversing methods may be chained together simply by using a dot in-between them.
- The code sample below uses both the .not() method and the .parent() method. Combined together this will only select the parent elements of div elements without a class of type or collection.

No comments:
Post a Comment